Noticeable needle loss or discoloration in pine trees could be a sign of a diseased tree. But what disease, and how can you treat your pine tree to restore it to health? So, if you’re asking yourself why your pine trees are turning brown, in this article, we’ll detail 10 common pine tree diseases and how to treat them.
We also have included a tree care expert’s comments on how to get your pine tree looking green again. After all, pines are evergreen trees, which means a healthy pine should stay green all year long.
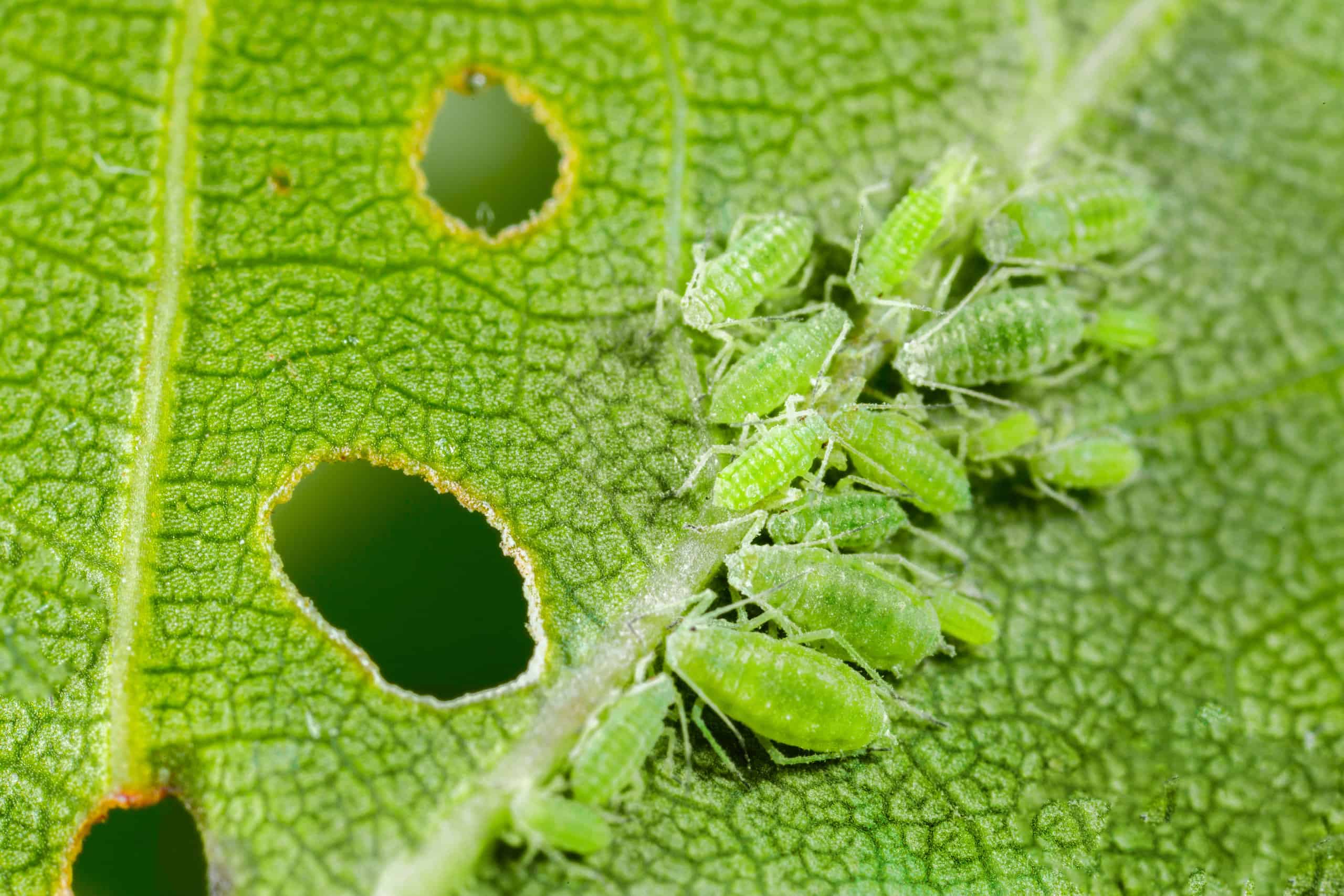
Austrian pine trees are a popular ornamental tree species due to their attractive evergreen foliage and ability to adapt to a range of climates. However, they can fall victim to sap-sucking aphids that cluster on the tender new growth and undersides of needles. Left uncontrolled, aphids weaken trees and cause leaf curl, stunting and honeydew secretions that promote sooty mold fungus. If your beautiful Austrian pine is infested with aphids, don’t panic. There are several effective, eco-friendly ways to eliminate these pesky bugs and restore your tree’s health.
Identifying Aphids on Austrian Pines
The first step is confirming you actually have aphids. Look for clusters of soft-bodied insects less than 1/8 inch long on the underside of needles and new shoots. Common colors include green, brown, black, pink, white, and yellow. The bugs have pear-shaped bodies and long legs and antennae. Check for symptoms like sticky honeydew and distorted, curled foliage.
Honeydew is the sugary waste excreted by aphids. It coats needles and drips onto lower branches and anything beneath the tree. Sooty black mold may colonize the honeydew, giving affected pine trees an ugly blackened appearance. Curled and stunted new growth also indicates aphid feeding activity.
Safest Control Methods for Aphids on Pines
If identified early aphid infestations can often be eliminated through safe non-toxic methods before significant damage occurs
Forceful Water Spray
A strong stream of water is highly effective at dislodging aphids from their feeding sites Focus on thoroughly spraying new shoots and undersides of infested needles with enough pressure to knock off bugs but not harm the tree Make sure to spray all areas of the canopy you can reach,
Pruning
Prune off heavily infested branches and dispose of properly to quickly reduce pest numbers. Only prune what’s necessary to remove concentrated populations. Never prune more than 1/3 of the live branches at one time.
Natural Predators
Encourage natural aphid predators like ladybugs, lacewings, hoverflies, and parasitic mini wasps. Avoid pesticides that kill beneficials. Plant varieties of flowers and herbs that attract predatory insects. Or purchase live lady beetles to release near infested pines.
Horticultural Oils and Insecticidal Soaps
Apply insecticidal soaps or lightweight horticultural oils like neem, canola, or jojoba oil to suffocate aphids on contact. Coat all infested needles for best results. Oils and soaps are affordable and safe for use any time. Avoid applying oils during the hottest days to prevent leaf burn.
When to Use Insecticides Against Severe Aphid Invasions
For moderate to severe infestations, or if the above methods fail, insecticide application may be warranted. Only consider insecticides if the infestation poses a serious threat to the long-term health of the tree. The safest products recommended for aphids on Austrian pines include:
-
Imidacloprid – Systemic insecticide applied as soil drench around tree. Transported through roots to needles making them toxic to sucking insects. Provides 1-2 months protection. May harm beneficial insects.
-
Insecticidal soap – Potassium salt sprayed directly on aphids disrupts cell membranes. Effective control with repeated applications. Biopesticide safe for people, pets, wildlife.
-
Horticultural oil sprays – Smother and kill insects on contact. Products containing neem oil also deter feeding. Eco-friendly and non-toxic to mammals.
-
Pyrethrins – Derived from chrysanthemum flowers, kills on contact. Often combined with piperonyl butoxide. Low toxicity to people and pets.
Always carefully follow label application rates and safety precautions when using pesticides. Systemic insecticides in particular should be applied with caution and as a last resort only. Consider hiring a professional arborist for insecticide application on large landscape pines.
Preventing Aphids from Returning
The best offense against aphids is maintaining healthy, vigorous trees that can resist attacks. Here are some tips to keep Austrian pines robust and discourage future infestations:
- Remove weeds, grass, and litter beneath tree – eliminates alternative hosts
- Apply 2-3″ organic mulch layer around root zone – retains moisture, insulates roots
- Water 1-2 times per week during drought – prevents stress making trees susceptible
- Avoid excess nitrogen fertilizer – causes overly succulent growth attractive to aphids
- Prune crossing branches and improve airflow – creates unfavorable conditions for aphids
- Monitor weekly and quickly respond to early signs of pests
- Encourage natural aphid predators with beneficial plants
- Apply horticultural oil spray in early spring to deter pests
With vigilance and using responsible, sustainable control methods, aphid infestations can be effectively eliminated from Austrian pines. Consistent monitoring, maintenance, and early intervention are key to protecting your investment and enjoyment of this versatile conifer. Don’t allow aphids to take over and compromise the beauty and longevity of your landscape pines.

Annosus Root Rot
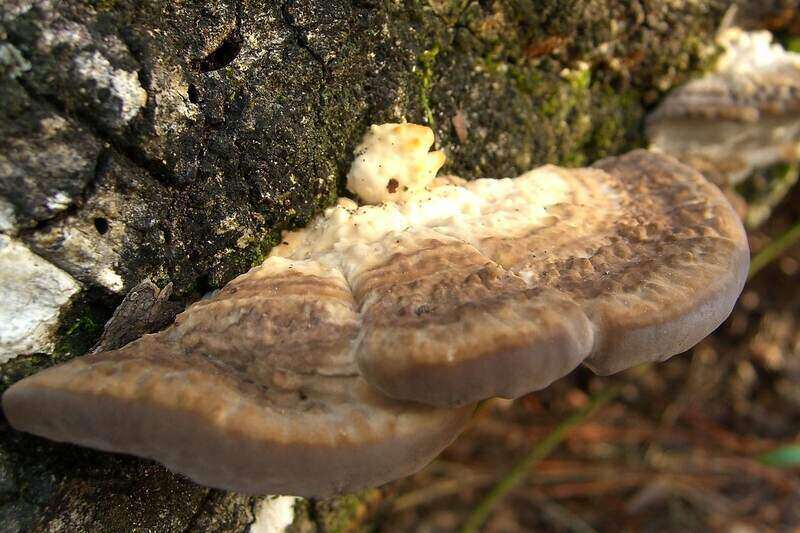

Annosus root rot stunts needle growth and causes a decaying condition called butt rot. This fungal disease is a concern in pine plantations where thinning has occurred. The freshly cut stumps following thinning encourage the spread of this disease. Although this disease leads to death, there is a solution to prevent it from spreading to healthy pines.
Pine trees affected: This disease affects these pine trees the most:
- Loblolly
- Slash pines
- White pines
Annosus root rot occasionally infects these pines:
- Shortleaf
- Longleaf
- Ponderosa
- Western white
- Lodgepole
- Whitebark
- Jack
- Pond
- Red
- Pitch
- Sand
- Virginia
Symptoms: Substantial stump decay will occur. The roots and butt develop a soft, stringy, white rot. The fungus may generate conks or fruiting bodies at the base of the trunk. These fruiting bodies vary in shape and are between gray-brown and dark-brown in color on their surface and white underneath.
Causes: The fungus, Heterobasidion annosum, spreads the most when stumps are freshly cut. Wind or splashing rain can carry the fungus from infected stumps to healthy trees with cut surfaces. After landing, the spores then penetrate the wood to establish an infection.
Infections can remain latent for decades before resuming growth in the pine tree. Stumps and trees with annosus root rot can also infect healthy trees through their roots.
Treatment: Common borax powder applied to the surfaces of freshly cut stumps will help prevent the spread to neighboring trees. Apply the borax powder in a salt shaker manner.
Seasons: Harvesting pines during dry summer and fall months lowers the possibility for spread.
Risk level: This disease is most concerning in forests following thinning, an operation that removes rows of trees. Trees of all ages can die from this disease, and volume losses from butt rot will occur in some species. In pines, death occurs after extensive decay.
Cotton Root Rot
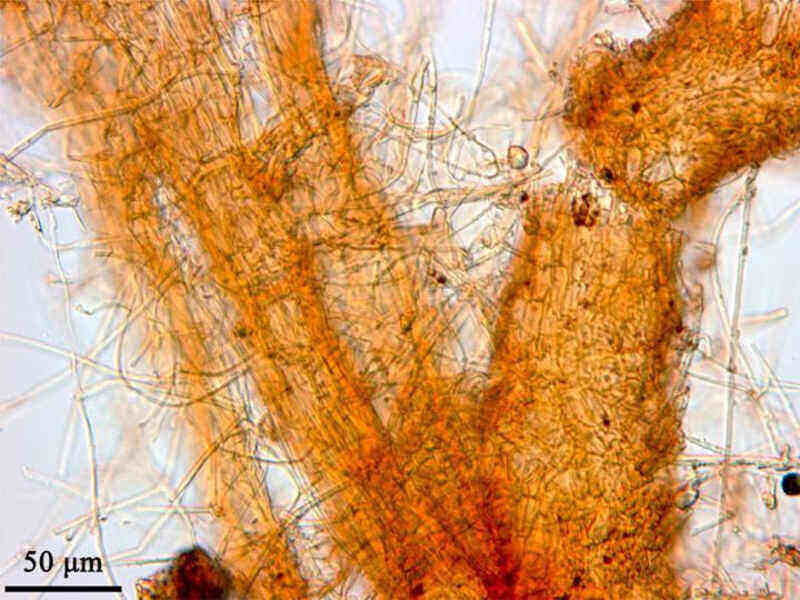
Cotton root rot is also known as Phymatotrichum root rot, Texas root rot, and Ozonium root rot. The fungal disease infects more than 2,000 species of plants and is one of the most challenging fungal diseases to control. Cotton root rot is most prominent in the Southwestern United States.
Pine trees affected: Pines exposed to high temperatures and alkaline soils or soils of limestone origin are most susceptible, such as Afghan pine.
Symptoms: Symptoms begin with a slight yellowing or bronzing of the host’s leaves. After three days, permanent wilting occurs, followed by death. Trees and shrubs will succumb to the disease more slowly. Affected areas appear as circular patterns of dead plants and can gradually enlarge over time.
Causes: Cotton root rot is caused by the fungus Phymatotrichum omnivorum. The fungus invades new areas by slow growth through the soil from plant to plant. The fungus can survive in the soil for many years and as far as 8 feet deep in the ground.
Treatment: If cotton root rot is infecting your pine, there is a chance of saving the tree if the decay is not yet substantial. The Oklahoma State University Extension recommends this process:
- Cover a ridge of soil around the tree’s drip line with a 2-inch layer of organic matter or cow manure.
- Scatter ammonium sulfate and sulfur over the manure.
- Flood the basin with enough water to soak the soil to a depth of 3 feet.
- Keep the soil moist for several weeks.
- The tree is likely to recover within the season.
Another solution is to plant a resistant grass crop around the infected area. The resistant crop creates a barrier that limits the spread of the disease.
Seasons: Symptoms usually occur from June through September when soil temperatures reach 82 degrees Fahrenheit.
Risk level: This fungal disease can survive in the soil for many years and kill even your tallest pine trees.

Damping-off is caused by a variety of pathogenic fungi, including Pythium sp., Rhizoctonia sp., Sclerotium sp., Fusarium sp., and Cylindrocladium sp. Proper prevention methods are the only way to save your pine seedlings from this disease. These pathogenic fungi usually live on dead organic matter in the soil.
Pine trees affected: Damping-off affects many plant seedlings. Most types of pine tree seedlings are susceptible to this disease.
Symptoms: Seedlings failing to emerge from the soil is a symptom of damping-off. If emerged, the lower stems of the seedling will collapse, and the seedling limps over. Seedling stems may appear water-soaked, soft, mushy, and discolored. Roots may appear absent or stunted.
Causes: These pathogenic fungi can attack young seedlings above, below, or at the soil line. The disease is most active in wet, moist soils. Pine seedlings are susceptible to the disease for a short period and will outgrow their vulnerability.
- Wind, insects, and water can all carry the infectious spores to the soil.
- Dirty hands, contaminated tools, or hose ends can add pathogenic fungi.
- Once introduced, the pathogens move from plant to plant.
- Low light, overwatering, and over-fertilization can add to the damping-off.
Treatment: Prevention is the best way to control damping-off in plant seedlings:
- Buy pine seedlings from nurseries with light, sandy soils that are less susceptible to pathogen growth.
- Raise the seedbeds so that they drain after irrigation and don’t remain too moist.
- Mulch the seedbeds with pine needles.
- Fumigate the soil with an approved soil fumigant before planting.
- Treat the seeds with a seed-protectant fungicide.
Seasons: Soil temperatures for damping-off vary depending on the pathogenic fungus.
Risk level: Damping-off is a common and fatal disease that affects all types of plant seedlings.
Foolproof Aphid Control and Prevention
FAQ
How do you treat aphids on pine trees?
Can a tree recover from aphids?
What can you spray on trees for aphids?
How to get rid of pine bark aphids?
How do you get rid of aphids on fruit trees?
Apply dormant oil. If aphids have settled on your fruit trees apply dormant oil, a commercial oil that controls pests during the off-season to kill eggs that are overwintering. Mix the dormant oil with water in a garden sprayer, according to the directions on the packaging, and apply to the leaves, stems, branches, and trunk of the tree.
Does Horticultural oil kill aphids?
If those don’t work for you, bring in the horticultural oil, which smothers and kills the insects on contact. Horticultural oil is extremely effective in controlling aphids, but only if you thoroughly treat the tree. Apply the oil in the dormant season to kill any overwintering eggs.
How do I get rid of aphids in my garden?
Apply the oil in the dormant season to kill any overwintering eggs. If needed, you can also use a lower rate of the oil during the growing season as well. Or there are insecticides that can be applied to the soil to treat for aphids if spraying isn’t viable.
Do Austrian pine trees die if left unprotected?
Left above ground and unprotected, a potted tree’s roots may die. The Austrian pine is prey to many fungal diseases, such as lophodermium needle cast, diplodia (sphaeropsis) tip blight, as well as various wood rots and decays. Remove affected branches as you spot them.
